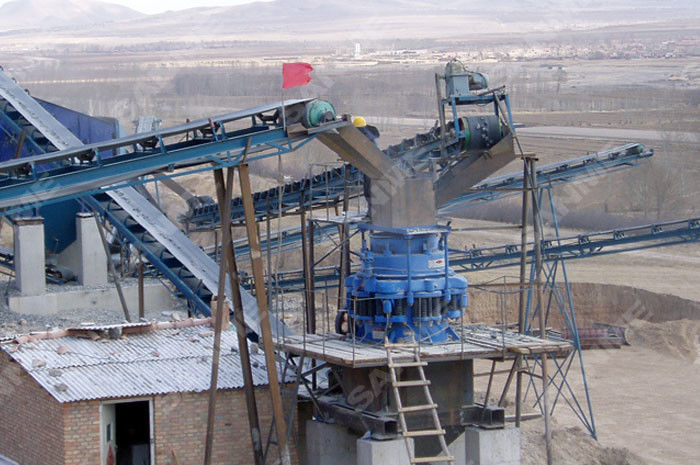

400Kw Metallurgy Feeding 460mm Cone Crusher Machine
2025-5-8
The components of the hydraulic system of a cone crusher mainly include the following core components. Different types of equipment (such as single-cylinder or multi-cylinder hydraulic cone crushers) may have differences in specific structures, but the basic functional modules have commonalities:
1、Hydraulic power and actuators
Hydraulic cylinder: As the core actuator, it drives the movable cone assembly through the telescopic movement of the cylinder piston rod to achieve discharge port adjustment, overload protection and cavity clearing functions. For example, in a single-cylinder hydraulic cone crusher, the bottom hydraulic cylinder controls the lifting and lowering of the movable cone through the hydraulic piston to complete iron protection and discharge port adjustment.
Hydraulic pump: Provides high-pressure hydraulic oil to the system to drive actuators such as cylinders. The flow and pressure parameters of the pump directly affect the system response speed and adjustment accuracy.
Hydraulic motor: Some models use hydraulic motors to drive transmission components, replacing traditional mechanical transmission methods to achieve stepless speed regulation and precise control.
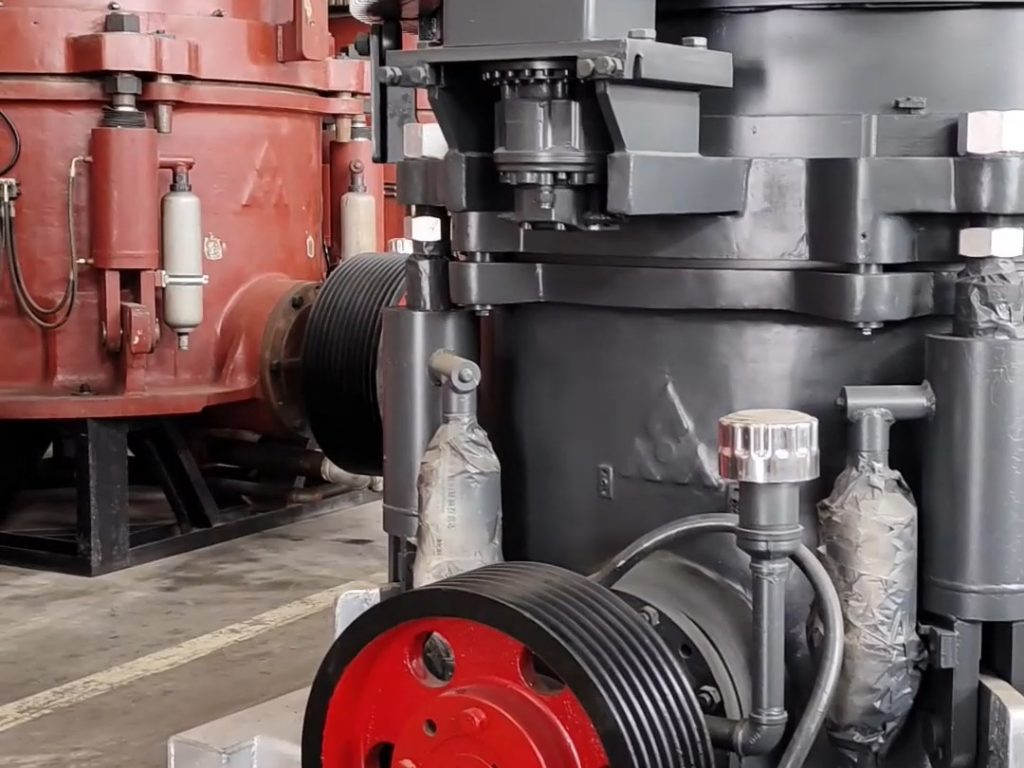
2、Hydraulic control components
Pressure valve and flow valve: Control the speed and strength of the cylinder by adjusting the system pressure and flow. For example, the overflow valve can prevent the system from overloading, and the throttle valve can adjust the moving cone movement rate.
Directional control valve: Control the flow direction of hydraulic oil to realize the switching of the cylinder’s telescopic, locking and other actions.
Accumulator: Store hydraulic energy, release energy when the system pressure suddenly changes, buffer the impact load, and protect the safety of the equipment. For example, in a multi-cylinder hydraulic cone crusher, the accumulator can absorb the hydraulic shock during overload.
3、Hydraulic auxiliary components
Oil tank: Store hydraulic oil, and have the functions of heat dissipation and precipitation of impurities.
Oil filter: Filter particulate contaminants in the hydraulic oil to prevent valve body jamming and cylinder wear.
Cooler: Control the temperature of the hydraulic oil to avoid high temperature causing the oil viscosity to decrease and the seal to age.
Pipes and joints: Connect various hydraulic components to ensure smooth oil transmission.
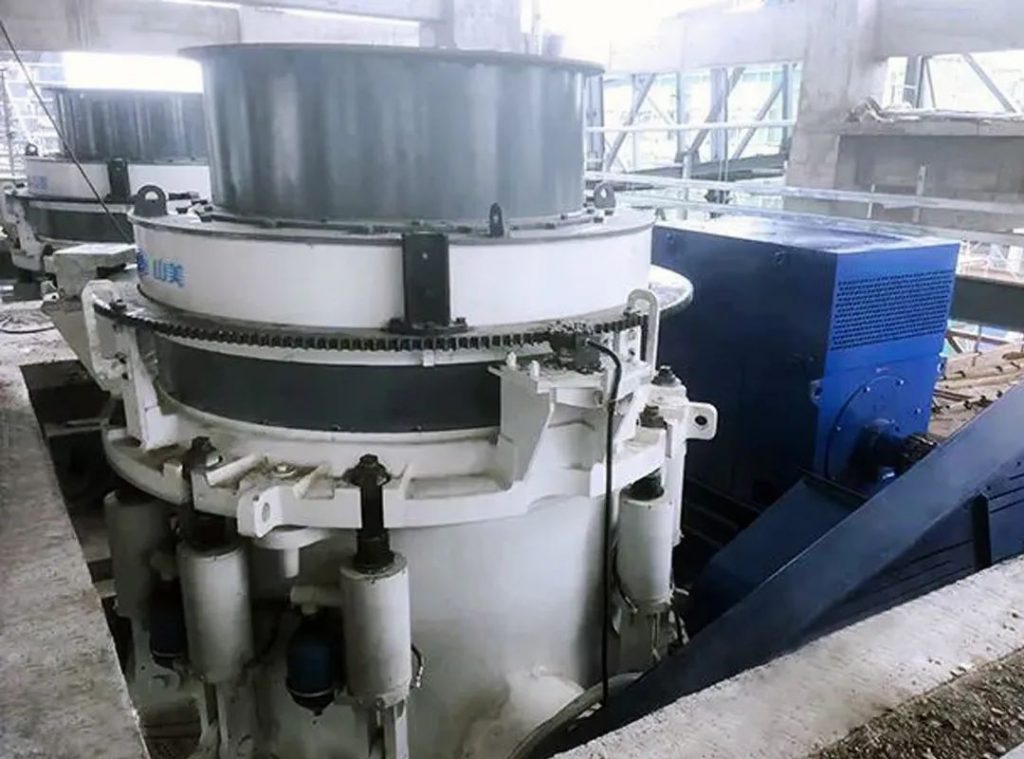

4、Sensors and monitoring devices
Pressure sensor: Real-time monitoring of system pressure to trigger overload protection action. For example, when the pressure exceeds the set value, the hydraulic system automatically increases the gap between the discharge port and discharges hard objects.
Displacement sensor: measures the displacement of the moving cone to achieve precise adjustment of the size of the discharge port.
Temperature sensor: monitors the temperature of the hydraulic oil to ensure that the system operates under appropriate working conditions.
5、Locking and protection device
Hydraulic locking cylinder: locks the position of the moving cone under normal working conditions to prevent vibration from causing changes in the discharge port. For example, in a single-cylinder hydraulic cone crusher, the locking cylinder is located between the locking ring and the adjustment ring, and the hydraulic pressure is used to keep the moving cone stable.
Overload protection valve: when an unbreakable object enters the crushing chamber, the pressure sensor triggers the overload protection valve to operate, and the hydraulic cylinder pushes the moving cone back to avoid equipment damage.
6、Lubrication and sealing system
Lubricating oil pump: provides lubricating oil to moving parts such as eccentric sleeves and main shafts to reduce wear. For example, in a multi-cylinder hydraulic cone crusher, the lubricating oil enters through the transmission shaft frame hole to lubricate the transmission bearings and gears.
Seals: prevent hydraulic oil leakage and external contaminants from invading to ensure system sealing.